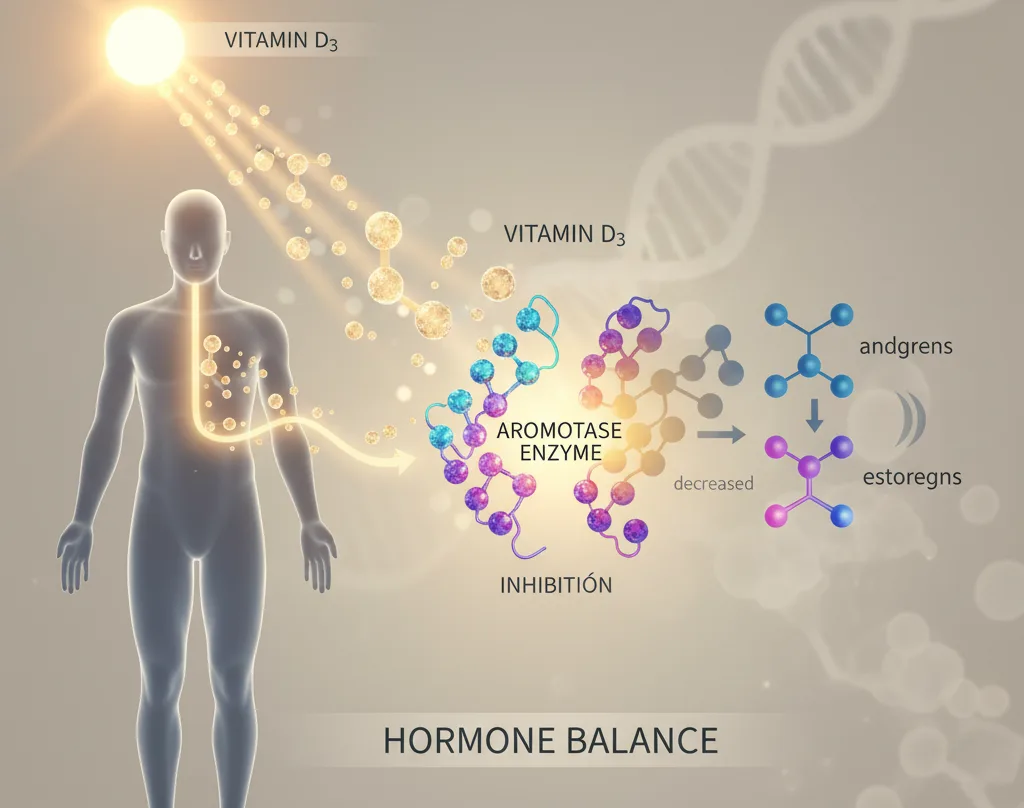
For decades, Vitamin D has been celebrated primarily for its crucial role in bone health. However, recent scientific inquiry is uncovering a much broader spectrum of influence for this vital nutrient, often dubbed the "sunshine vitamin." Among these emerging insights is its potential to modulate hormone pathways, specifically through the inhibition of the aromatase enzyme.
What is Aromatase and Why Does it Matter?
At the heart of this discussion is aromatase (CYP19A1), an enzyme belonging to the cytochrome P450 family. Its primary function is to convert androgens (male sex hormones like testosterone) into estrogens (female sex hormones like estradiol). This conversion process is essential for normal physiological function in both men and women.
However, an imbalance or excessive activity of aromatase can have significant health implications:
-
In Women: Overactive aromatase can lead to higher estrogen levels, which are implicated in the development and progression of estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancers.
-
In Men: Similarly, excess aromatase activity can result in elevated estrogen and decreased testosterone, potentially leading to issues like gynecomastia (enlargement of male breast tissue), reduced libido, and other complications, particularly in individuals using exogenous steroids.
Vitamin D3 and Aromatase: The Research Connection
A key study, "Vitamin D analog EB1089 inhibits aromatase expression by dissociation of comodulator WSTF from the CYP19A1 promoter—a new regulatory pathway for aromatase," published in Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research in 2013, highlighted this intriguing connection.
The research indicated that a Vitamin D analog (EB1089) could inhibit aromatase activity and expression. This occurs through a novel mechanism involving the dissociation of a comodulator (WSTF) from the CYP19A1 promoter, essentially dampening the production of the aromatase enzyme itself. While this particular study focused on a Vitamin D analog and its effects on breast cancer cells, its findings open the door to understanding how Vitamin D3 might naturally influence similar pathways.
Implications for Health: Beyond Bone Density
Drawing on such research, the implications of Vitamin D3's potential to reduce aromatase activity are far-reaching:
1. Women's Health and Breast Cancer Risk
For women, especially those at risk of or undergoing treatment for estrogen-sensitive breast cancer, modulating estrogen levels is a critical strategy. By potentially reducing aromatase activity, Vitamin D3 could contribute to a more balanced estrogen environment, thereby lowering the risk of developing breast cancer or aiding in its management. It's important to note that while promising, Vitamin D3 would be considered a supportive measure, not a standalone treatment.
2. Men's Health and Hormone Balance
In men, particularly those who engage in practices that can disrupt natural hormone balance (such as the use of performance-enhancing steroids), controlling estrogen levels is crucial. An increase in androgens (either naturally occurring or exogenous) can lead to a compensatory increase in estrogen via aromatase, resulting in undesirable side effects like gynecomastia or water retention. Vitamin D3's role in inhibiting aromatase could therefore help to mitigate these estrogen-related side effects, supporting overall hormonal health.
The Bigger Picture: Lifestyle and Supplements
While the research is compelling, it's crucial to understand that maintaining optimal Vitamin D levels is part of a broader health strategy. Exposure to sunlight remains the primary natural source of Vitamin D3, synthesized in the skin. However, dietary intake (from fatty fish, fortified foods) and supplementation are often necessary, especially in regions with limited sun exposure or for individuals with specific health needs.
It is important for anyone considering Vitamin D supplementation for hormone regulation or disease prevention to consult with a healthcare professional. While generally safe, excessive Vitamin D intake can have adverse effects, and individualized guidance is always recommended.
Conclusion
The emerging understanding of Vitamin D3's role in inhibiting the aromatase enzyme adds another layer to its already impressive health benefits. From supporting women in managing breast cancer risk to helping men maintain hormonal balance, the "sunshine vitamin" continues to reveal its multifaceted importance. As research progresses, we can anticipate even deeper insights into how this humble vitamin profoundly influences our health at a fundamental, hormonal level.