In the world of nutrition and fitness, the debate between meat protein and vegetable protein is a hot topic, especially on social media. A common, but flawed, comparison often circulates, claiming that a certain amount of calories from meat and a similar amount from vegetables like broccoli yield the same amount of protein. However, this comparison overlooks two critical factors: the basis of measurement and the quality of the protein.
The Flaw in Calorie-Based Comparisons
The first mistake in many online comparisons is using calories instead of weight (grams). While 100 calories of meat might have a similar protein count to 100 calories of broccoli, this is not an accurate way to compare their nutritional value. Calories are a measure of energy, not mass. A more useful comparison uses a consistent weight.
For example, let's look at a 100-gram serving:
100 grams of meat contains approximately 22 grams of protein and around 250 calories.
100 grams of broccoli contains about 2.5 grams of protein and only 31 calories.
This means that to get the same amount of protein as a 100-gram serving of meat, you would need to consume nearly a kilogram (1000 grams) of broccoli.
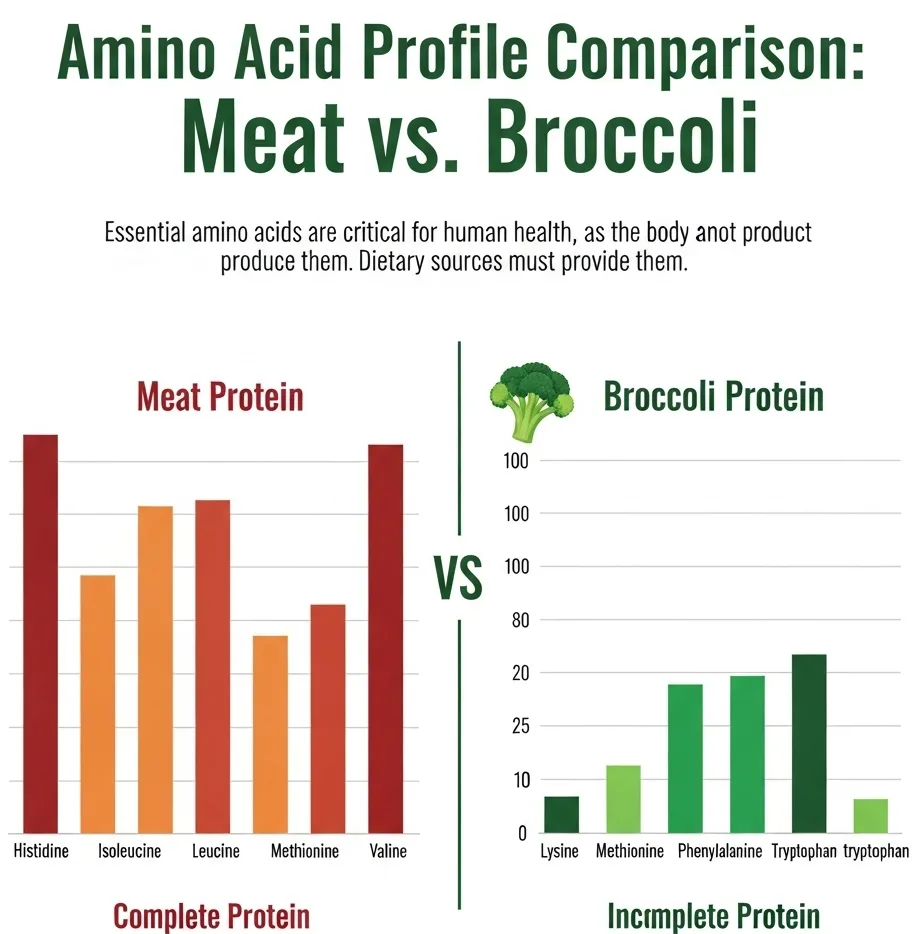
The Importance of Protein Quality
The second, and perhaps more important, factor is the quality of the protein. Protein quality is determined by two main things: the amino acid profile and digestibility.
Amino Acid Profile: Our bodies need a variety of amino acids to function properly. Complete proteins contain all nine essential amino acids that the human body cannot produce on its own. Meat is an excellent example of a complete protein. Most plant-based proteins, with a few exceptions like quinoa and soy, are incomplete proteins, meaning they lack one or more of these essential amino acids.
Digestion Quality: The body's ability to break down and absorb protein is known as protein digestibility. Animal proteins are generally much easier for the body to digest and utilize than plant proteins. For example, the protein digestibility of meat is typically over 90%, while some plant proteins can have lower digestibility due to components like fiber that can interfere with absorption.
This doesn't mean you should avoid vegetables like broccoli. They are packed with vitamins, minerals, and fiber and are an essential part of a healthy diet. This comparison simply highlights that when the goal is to consume a high amount of quality protein, meat is a far more efficient source.