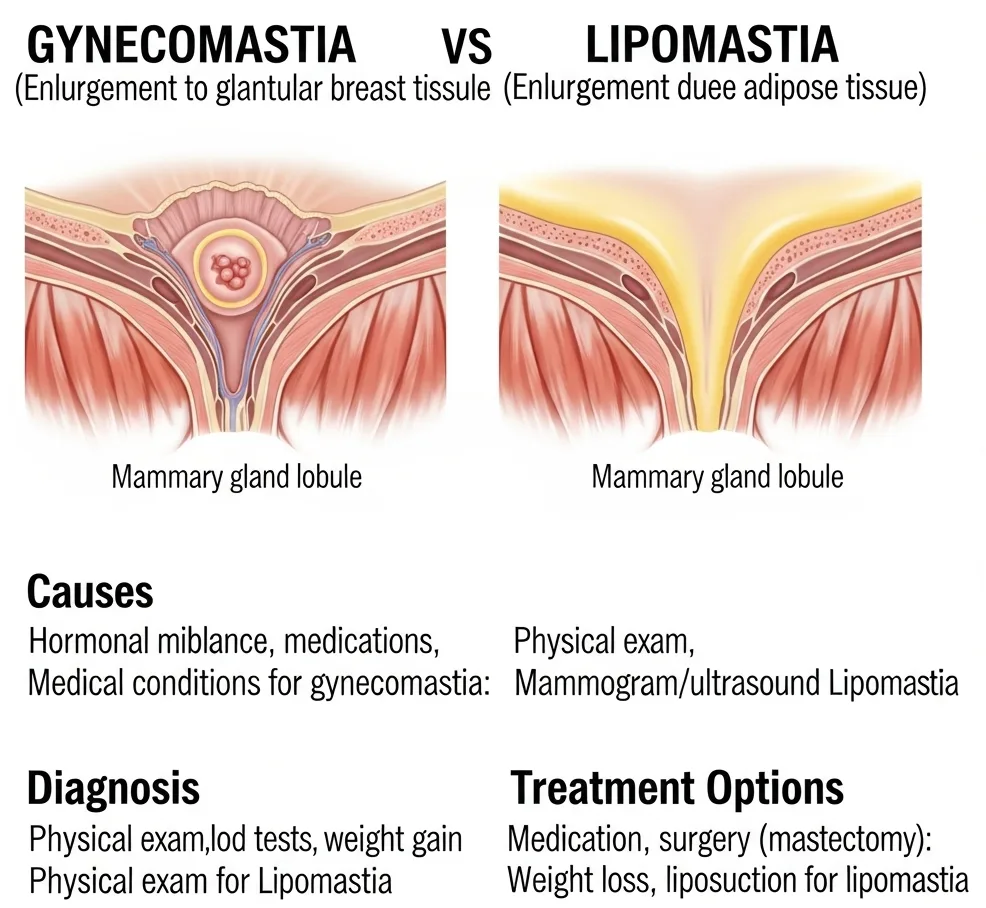
Gynecomastia vs. Lipomastia: A Comprehensive Guide Understanding the difference between gynecomastia and lipomastia is the crucial first step in finding the right treatment. While both conditions involve enlarged breast tissue in men, their causes and treatments are very different.
What is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is the enlargement of the male breast due to an increase in glandular (breast) tissue. It is often caused, directly or indirectly, by an increase in estrogen levels. The defining characteristic is the presence of a firm, glandular mass, typically 4 cm or larger.
Key points about Gynecomastia:
Causes: In addition to physiological reasons (common during puberty), it can be triggered by certain medications (like Spironolactone), anabolic steroid use, or underlying conditions like liver or kidney disease.
Diagnosis: After ruling out other causes, a diagnosis involves a thorough evaluation, including hormone tests for testosterone, LH, SHBG, HCG, and estradiol.
Pubertal Gynecomastia: This form typically appears around age 14 and resolves on its own within one to two years in 90% of cases. However, if it persists past age 18, it is considered permanent.
Treatment: In the first six months, especially if there is pain, medication like Tamoxifen (20 mg daily) can help reduce pain and size. However, after six months, medication is usually ineffective.
Surgical Intervention: Once the initial six-month period has passed and pain has subsided, surgery is often the only effective treatment. It is primarily an aesthetic procedure and does not pose any health risks.
What is Lipomastia?
Lipomastia is the enlargement of male breasts due to an accumulation of fatty tissue, not glandular tissue. It is not caused by hormonal imbalances and is commonly seen in overweight individuals.
Key points about Lipomastia:
Appearance: The mass is soft and consists of fat tissue, unlike the firm, glandular mass of gynecomastia.
Treatment: Lipomastia can often be significantly reduced with exercise and weight loss. If these methods are not enough, it can be treated with liposuction or other surgical fat removal procedures.
Medication: Medications like Tamoxifen or Letrozole, which target hormonal pathways, are completely ineffective for lipomastia.
Key Differences and Misconceptions
The main difference between the two conditions is the type of tissue involved: glandular tissue for gynecomastia and fatty tissue for lipomastia. A common mistake is to misdiagnose lipomastia as gynecomastia. It's essential to understand that while both can be a source of aesthetic concern, neither poses a significant health risk. However, only surgery can address gynecomastia, whereas lipomastia may respond to lifestyle changes.